Chapter 34
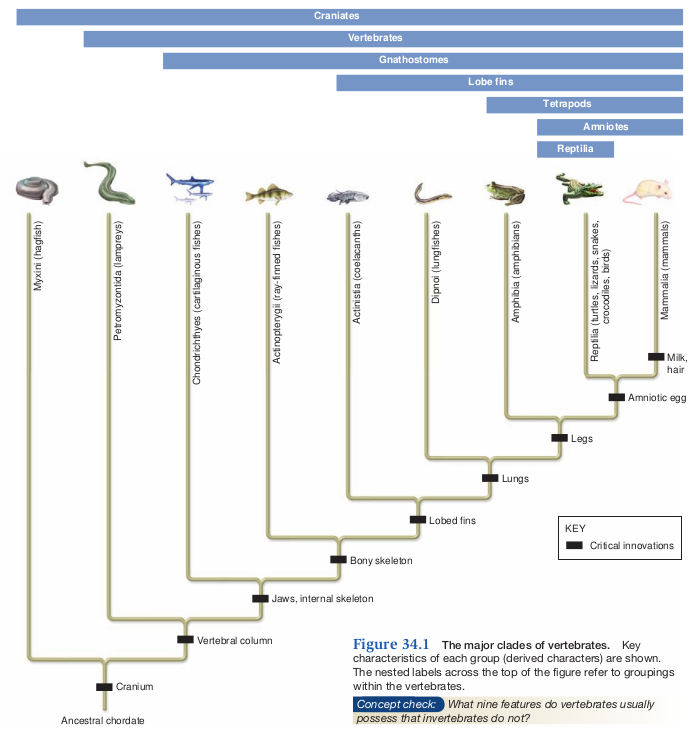
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Vertebrates
- Chordates with a backbone
Chordate features as well as:
- Vertebral column
- Series of cartilaginous or bony elements
- Cranium
- Endoskeleton or cartilage or bone
- Hox genes (lots of them)
- Neural crest
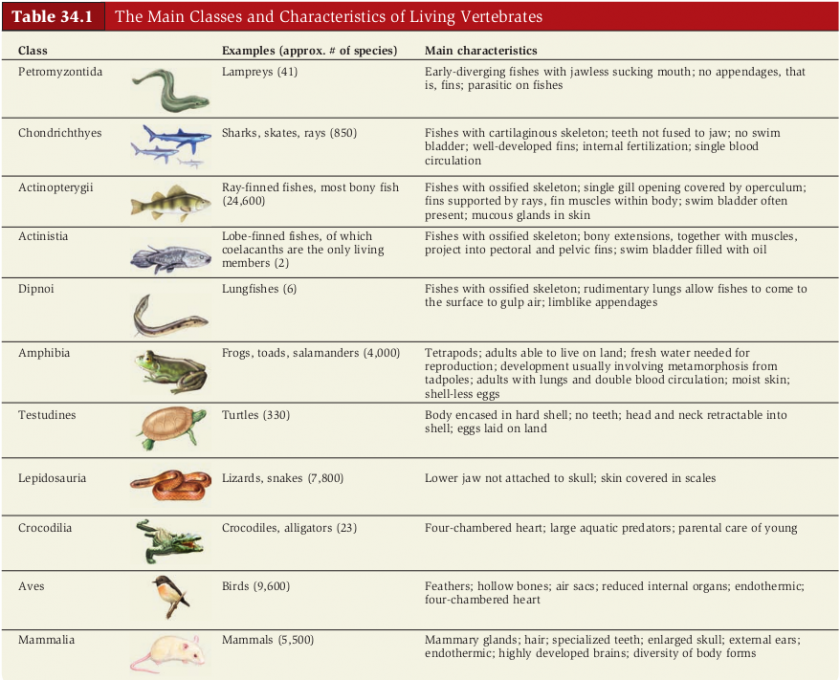
Cyclostomes
- Jawless Fishes
Class Myxini
- Hagfishes
- lack jaws, eyes, fins vertebrae
- skeleton comprised of notochord and cartilaginous skull
- covered in slime
Class Cephalospidomorphi
- Lampreys
- Has notochord, and cartilaginous vertebral column
- lacks jaws and appendages (fins)
- Oldest fossil records 510 mybp
Class Chondrichthyes
- Cartilaginous fishes
- Sharks, skates, rays
- Cartilaginous skeleton and notochord as adults
- jawed fishes
- paired appendages (fins)
- < 900 species
Class Osteichthyes
- Bony fishes
- Most diverse vertebrate group with < 26,000 species
- Bony skeleton (most do have this)
- Jawed
- paired appendages (fins)
Tertapod: Gnathastomes
- Four limbs with jawed mouth
- Transition to land involved adaptions for locomotion, reproduction, desiccation (drying out) prevention, and gas exchange
- Sturdy lobe-finned fishes became animals with four limbs
- Vertebral column strengthened, ship and shoulder bones braced against backbone
- relatively simple changes in gene expression, especially Hox genes
Class Amphibia
- >4000 species
- Amphibios
- greek - "living double life"
- split their life between aquatic and terrestrial stages
- Successfully invaded land but reproduce in water
- Lunges are and adaption to semi-terrestrial lifestyle
- Three chambered heart
- Fishes only have a two chambered heart
- External Fertilization
- Larval stages are aquatic
- Undergo metamorphosis
- Not completely separated from water
Order Anura
- Frogs and toads
- Nearly 90% of amphibians
- Carnivorous adults
- Herbivorous tadpoles
Order Apoda
- Caecilians
- Nearly blind tropical burrowers
- Secondarily legless
Order Urodela
- Salamanders
- Often have colorful skin patterns
- Most have four limbs
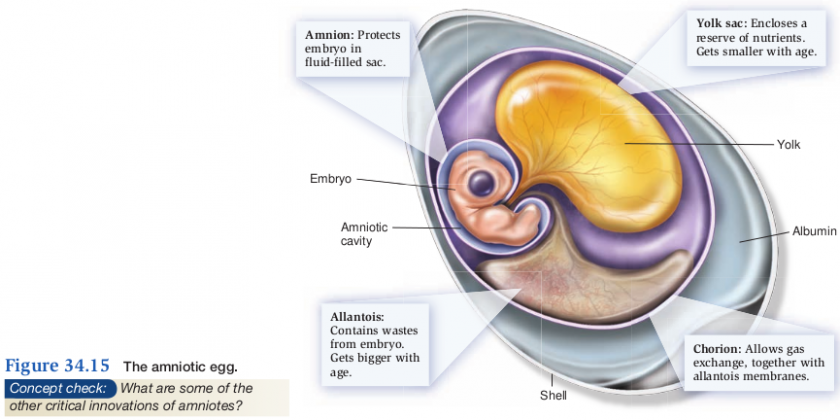
Amniotes
- Tetrapods with a desiccation resistant egg
- Critical innovation
- Development of a shelled egg
- Amniotic egg
- Broke the tie to water
- Three internal membranes
- Shell is permeable to Oxygen and CO2
- Birds
- Hard and Calcareous
- Reptiles
- Soft and Leathery
- Most Mammals
- Embryo embeds in uterine wall
- Only three species lay eggs
- These eggs are soft and leathery
- Birds
Other Key Innovations of the Amniotes
- Desiccation resistant skin
- contains keratin
- Thoracic breathing
- Negative pressure sucks air in
- Water conserving Kidneys
- Concentrate waste prior to elimination
- Internal fertilization
Class Reptilia
- >8000 living species
- turtles, crocodilians, lizards, snakes
- Can live away from water
- thicker skin and scales
- larger brain
- larger limbs with muscles
- enhanced kidneys
- Amniotic egg
- "indoor pond"
Vertebrate Reproductive Modes
- Oviparous
- Egg laying outside of the body
- Ovoviviparous
- live baring wuth retention of eggs
- No maternal connection
- Viviparous
- live bearing with egg retained
- Maternal connection
Class Aves
- Birds
- Evolved form small dinosaurs
- Fossils 150mybp
- Adaptions for flight
- Feathers
- Modified front limbs
- Lightweight skeleton
- Organ reduction
- Lungs and air sacs
- more gas exchange
- Oviparous
- all leg layers
- Bill beak
- Encloses mouth and nasal cavity
- Adapted for environment
Endothermic
- "Internal temperature"
- Body temperature is primarily controlled by trapped metabolic heat.
- Birds and mammals
Ectothermic
- "External temperature"
- Body temperature is primarily related to external temperature
- Metabolic heat is generated but difficult to capture/maintain the heat
- Fishes, amphibious, reptiles
Class Mammalia
- Milk producing Amniotes
- Evolved from amniote ancestors (reptiles) earlier than birds
- >6000 species
- Appeared ~ 225mybp
- Evolved from small mammal-like reptiles
- After dinosaur extinction, mammals flourished
- Range of sizes, body forms, and complexity unmatched
- Fish-like mammals
- Marine mammals
- Bird-like mammals
- Bats
- Reptile-like mammals
- Three egg layers
Distinguishing Characteristics
- Mammary Glands
- Secrete milk
- All have hair
- In varying amounts
- Only vertebrate with multiple dentitions
- Heterodont
- Different types of teeth
- incisors, canines, molars, premolars
- Thecodont
- Teeth with long roots embedded in sockets of jawbone
- Diphyodont
- Milk teeth that are mostly replaced by "adult" teeth later in life
- Heterodont
- Pinna
- Flap of cartilage and lose connective tissue to channel and funnel sound
- The "outer ear"
- Three middle ear ossicles (bones)
- Enlarged Skull
- Brain enlarged in large skull
- Larger Cerebrum
- Single lower Jawbone (Dentary)
- Anucleate red blood cells
Order Primates
- Primarily tree dwelling species
- grasping hands with opposable thumbs
- Large brain
- Some digits with flat nails
- Not claws
- Binocular vision
- Complex social behavior and well-developed parental care
- Enhanced sense of touch
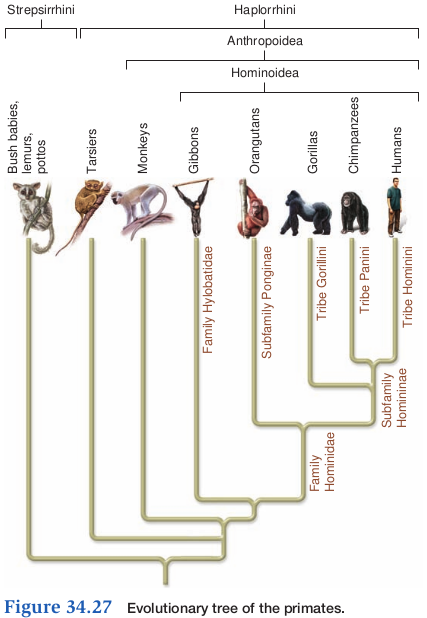
Taxonomy of Humans
-
Kingdom Animalia
-
Phylum Chordata
-
Subphylum Vertebrata
-
Class Mammalia
-
Order Primates
-
Suborder Anthropoidea
-
Superfamily Hominoidae
-
Family Hominidae
-
Subfamily Homininae
-
Tribe Hominini
-
Genus Homo
- Species Homo sapiens
-
Genus Homo
-
Tribe Hominini
-
Subfamily Homininae
-
Family Hominidae
-
Superfamily Hominoidae
-
Suborder Anthropoidea
-
Order Primates
-
Class Mammalia
-
Subphylum Vertebrata
-
Phylum Chordata