Chapter 35
Introduction to Plants
Kingdom Plantae
- We will primarily be discussing the angiosperms
- Phylum Anthophyta
- Flowers and fruits
- Only group that doe/has these things
- Advanced traits
- Seeds
- Advanced vascular tissues
From seed to seed
The life of a flowering plant
- Seeds
- reproductive structures produced by angiosperms and other seed plants
- usually the result of sexual reproduction
- contains embryos that develop into seedlings upon germination
- has survival value
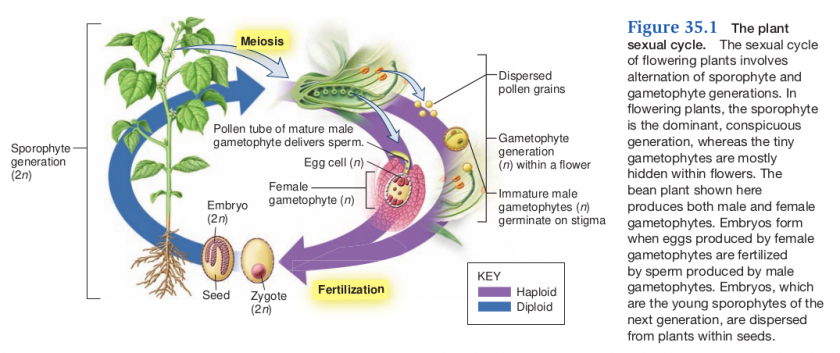
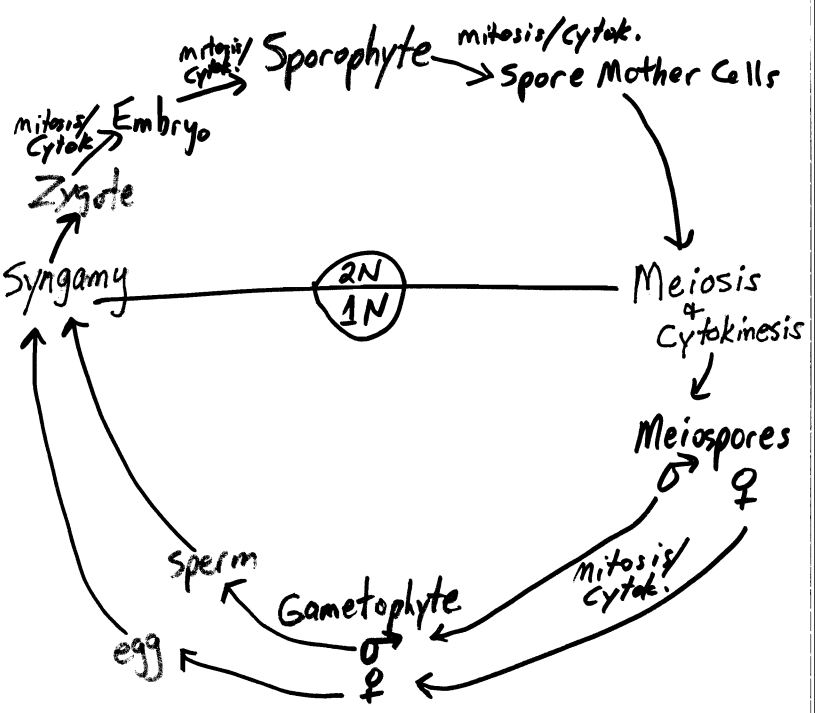
Alternation of Generations
- Exhibited by all plants (and plant-like organisms) that have sexual reproduction
- There is an alternation between a diploid (2N) form [sporophyte] and a haploid (1N) form [gametophyte]
Gametophyte (haploid)
- Gamete-producing plant fomr
- multicellular
- microscopic in flowering plants
- female
- embryo sac with egg
- male
- pollen grain
- female
- grow and develop within flowers of angiosperms
- produces gametes by mitosis/cytokineses
Sporophyte (diploid)
- multicellular
- large "plant" in flowring plant
- produces haploid spores by meiosis (reduction)
- called meiospores
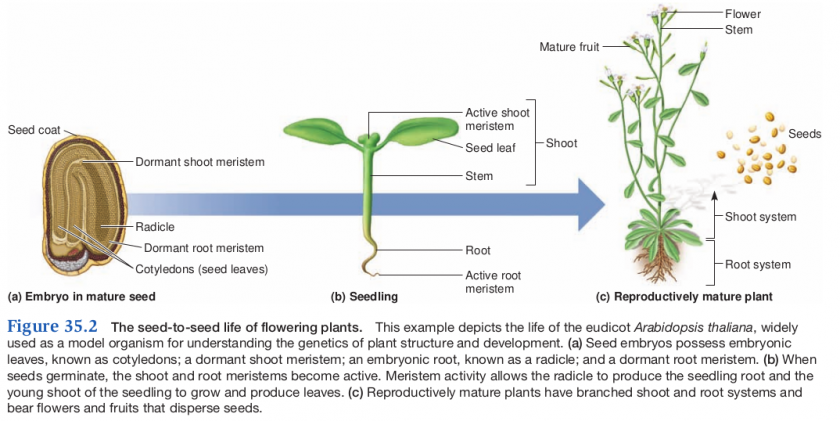
The plant embryo
- Fertilization (syngamy) results in the formation of a diploid zygote, which undergoes mitosis to form an embryo (multicellular)
- the embryo is a sporophyte that lies dormant in the seed with a supply of stored food and a seed coat
- may lay dormant for long periods until conditions are favorable
The plant body
Composed of three organ types
- stems
- leaves
- roots
Shoot system
- stem
- produce leaves and branches and bear the reproductive structures
- leaves
- flattened structure specialized for photosynthesis
Root system
- roots
- Provide anchorage in the soil and foster efficient uptake of water and minerals
- can store food
Growth
- Indeterminate growth
- increasing in size as long as the plant is alive
- grows into a seedling and then a mature plant
- Plant growth occurs by 3 means
- Increase in number of cells
- cellular reproduction
- (mitosis/cytokineses)
- cellular reproduction
- increase in cell size
- elongation
- increase in weight/mass
- Increase in number of cells
Development
- Mature plants produce reproductive structures
- flowers
- seeds
- fruits
- flowers and floral buds are reproductive shoots that develop when shoot apical (tip) meristems produce flower parts instead of new tissues and leaves
- flowers are produced by determinate growth
Seed coats
- Flower tissues enclose and protect tiny male and female gametophytes
- sperm in pollen fertilizes the egg, triggering ovules to develop into seed and flower parts to develop into fruit
- fruits enclose seeds and function in seed dispersal
- Angiosperms
Meristems
- Seedlings and mature plants produce new tissue from meristems
- cell factories
- meristem is a region of undifferentiated cells that produce new tissue by cell division
- A dormant meristem occurs at the shoot and root of seed embryos
- activate in seedlings
- mature plants have shoot apical meristems (SAM) and root apical meristems (RAM)
Mature sporophyte develop from seedlings
- photosynthesis powers the transformation