Chapter 35
Introduction to Plants
Kingdom Plantae
- We will primarily be discussing the angiosperms
- Phylum Anthophyta
- Flowers and fruits
- Only group that doe/has these things
- Advanced traits
- Seeds
- Advanced vascular tissues
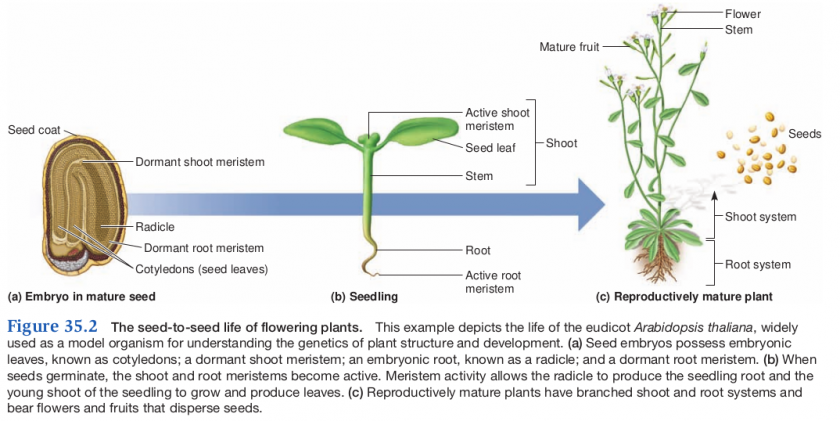
From seed to seed
The life of a flowering plant
- Seeds
- reproductive structures produced by angiosperms and other seed plants
- usually the result of sexual reproduction
- contains embryos that develop into seedlings upon germination
- has survival value
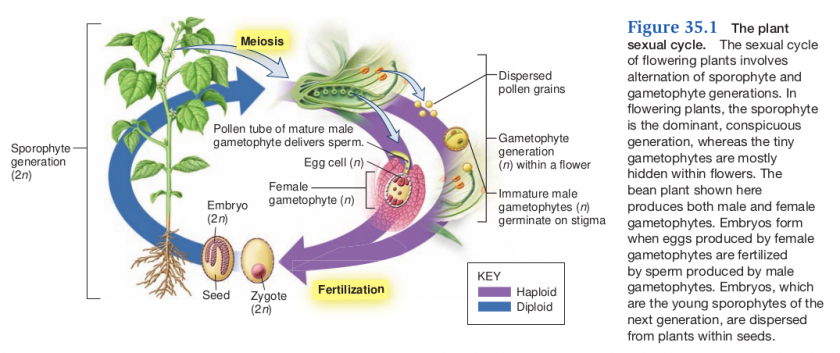
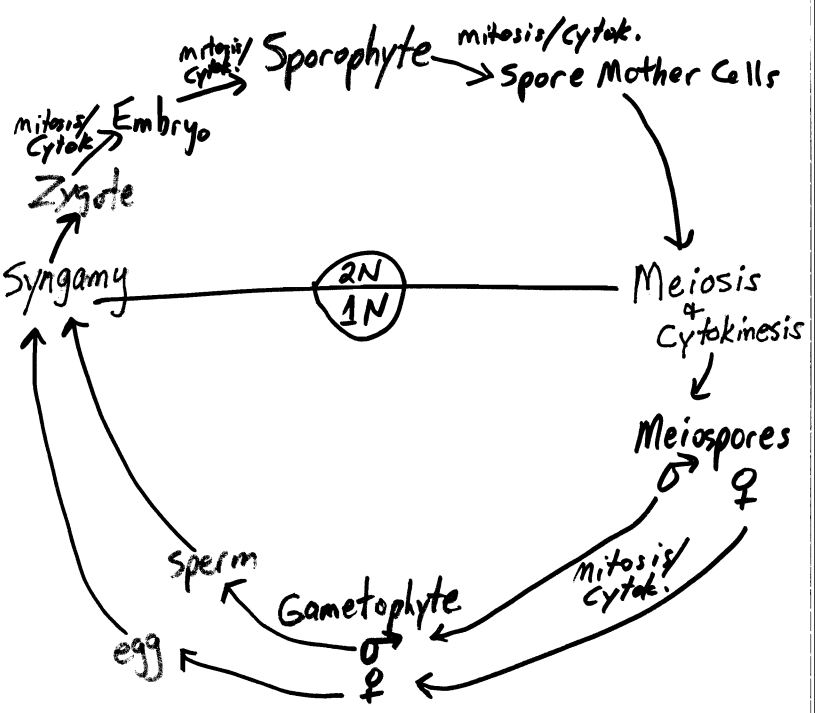
Alternation of Generations
- Exhibited by all plants (and plant-like organisms) that have sexual reproduction
- There is an alternation between a diploid (2N) form [sporophyte] and a haploid (1N) form [gametophyte]
Gametophyte (haploid)
- Gamete-producing plant fomr
- multicellular
- microscopic in flowering plants
- female
- embryo sac with egg
- male
- pollen grain
- female
- grow and develop within flowers of angiosperms
- produces gametes by mitosis/cytokineses
Sporophyte (diploid)
- multicellular
- large "plant" in flowring plant
- produces haploid spores by meiosis (reduction)
- called meiospores
The plant embryo
- Fertilization (syngamy) results in the formation of a diploid zygote, which undergoes mitosis to form an embryo (multicellular)
- the embryo is a sporophyte that lies dormant in the seed with a supply of stored food and a seed coat
- may lay dormant for long periods until conditions are favorable
The plant body
Composed of three organ types
- stems
- leaves
- roots
Shoot system
- stem
- produce leaves and branches and bear the reproductive structures
- leaves
- flattened structure specialized for photosynthesis
Root system
- roots
- Provide anchorage in the soil and foster efficient uptake of water and minerals
- can store food
Growth
- Indeterminate growth
- increasing in size as long as the plant is alive
- grows into a seedling and then a mature plant
- Plant growth occurs by 3 means
- Increase in number of cells
- cellular reproduction
- (mitosis/cytokineses)
- cellular reproduction
- increase in cell size
- elongation
- increase in weight/mass
- Increase in number of cells
Development
- Mature plants produce reproductive structures
- flowers
- seeds
- fruits
- flowers and floral buds are reproductive shoots that develop when shoot apical (tip) meristems produce flower parts instead of new tissues and leaves
- flowers are produced by determinate growth
Seed coats
- Flower tissues enclose and protect tiny male and female gametophytes
- sperm in pollen fertilizes the egg, triggering ovules to develop into seed and flower parts to develop into fruit
- fruits enclose seeds and function in seed dispersal
- Angiosperms
Meristems
- Seedlings and mature plants produce new tissue from meristems
- cell factories
- meristem is a region of undifferentiated cells that produce new tissue by cell division
- A dormant meristem occurs at the shoot and root of seed embryos
- activate in seedlings
- mature plants have shoot apical meristems (SAM) and root apical meristems (RAM)
Mature sporophyte develop from seedlings
- photosynthesis powers the transformation of seedlings into mature plants
- provides the ability to produce organic food
- plants undergo both vegetative growth and reproductive development
Hierarchy of structures in a mature plant
- Specialized cells
- tissues
- organs
- organ systems
- branches, buds, flowers, seeds, fruits
- root and shoot systems
- plant (the organism itself)
Primary Growth
- Elongation of plant organs
- roots, stems, and leaves
- Occurs in ALL plants
- Produces primary tissues from apical meristems (SAM and RAM)
Primary Tissues
- Primary xylem
- vascular/conducting tissue
- water and minerals
- Primary phloem
- vascular/conducting tissue
- food and solutes
- Epidermis
- dermal
- Outter-most tissue
- protection
- holds water in plant
- dermal
- Support ground tissues
- Parenchyma
- most abundant type
- storage
- water and food
- part of cortex/pith
- Collenchyma
- Protection/support of growing plant organs
- cortex
- Sclerenchyma
- protection/support of non-elongating organs
- cortex
- Parenchyma
Secondary Growth
- Expansion of plant organs
- lateral meristems
- roots and stems only
- does not occur in leaves
- noes not occur in all plants
- Produces secondary tissues
- woody tissues
Major groups of Angiosperms
Eudicots
- >240,000 species
- all have primary growth
- most have secondary growth
- for this class we are saying they all have secondary growth
Monocots
- >60,000 species
- all have primary growth
- very few have secondary growth
- for this class we are saying that non have secondary growth
- grasses, corn, tulips, lilies
Root system adaptations
Major functions
- absorbing water and minerals
- anchoring the plant in the soil
- storing nutrients and water
Eudicots
Taproots
Monocots
fibrous roots
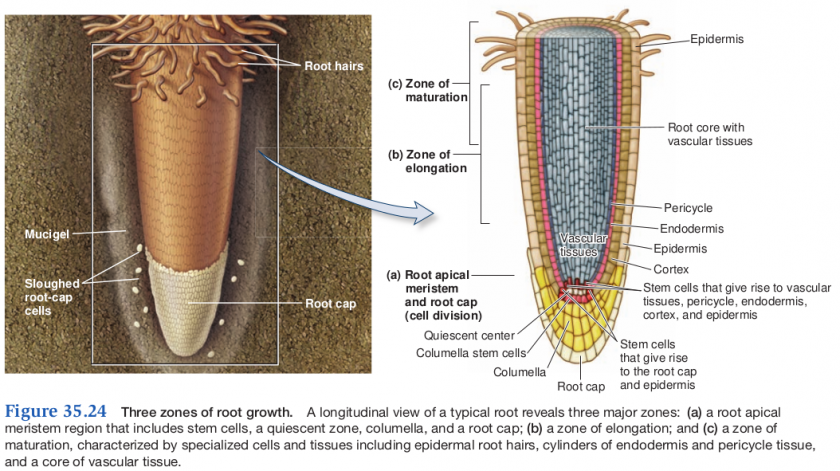
Three zones of root growth
- Region of cell division
- RAM and root cap
- RAM contains cells that ar dividing
- Quiescent center keeps nearby cells undifferentiated
- Root cap embedded in mucigel
- Mucigel is a slimy substance that covers the root cap of the roots of plants.
- Region of elongation
- cells extend by uptake of water
- Region of maturation
- root cell differentiation and tissue specialization
- identified by presence of root hair
- water and mineral uptake
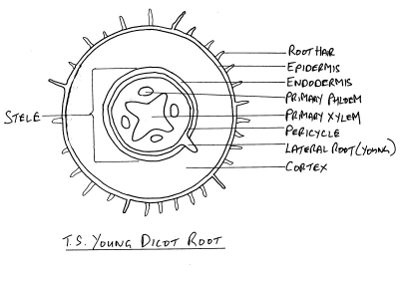
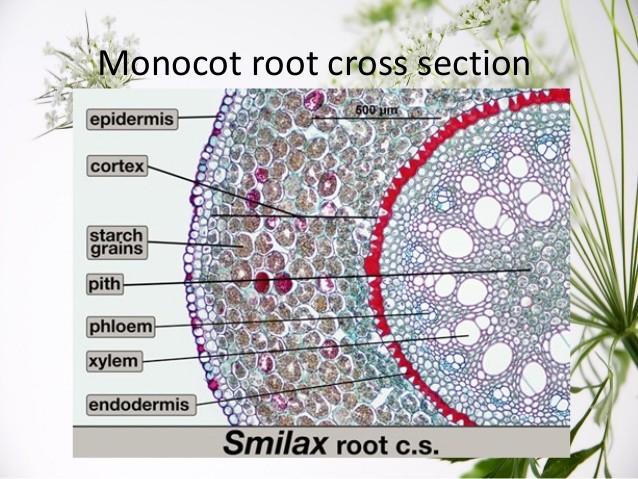
Root Internal Structure
- Epidermis of mature roots encloses a cylinder of parenchyma called the root cortex
- One cell thick
- often rich in starch
- functions as food storage
- many contain inter-cellular air spaces
- Endodermis
- selective absorption of minerals
- one cell thick
- Meristematic pericycle
- encloses root in vascular tissues
- provides lateral branches
- woody roots produce primary vascular tissues followed by secondary vascular tissues
Eudicot root
Monocot Root
The shoot system
Stem and leaf adaptations
Shoots are modular with 4 parts
- Stem node
- leaves or branches emerge
- Internode
- stem between adjacent nodes
- elongation
- Leaf
- Axillary Meristem
- generate axillary buds
- can produce flowers or branches
- Lateral shoots
- New branches bear SAM at their tips
Shoot Tip
- Terminal bud
- at the end of each shoot
- includes the SAM and other parts
- scales
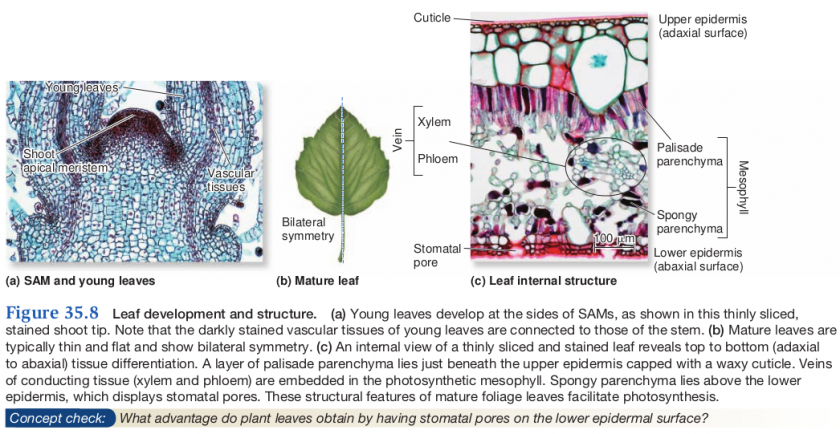
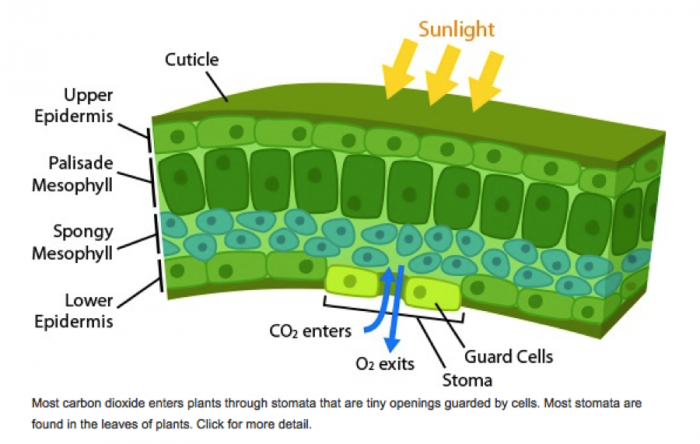
Leaf anatomy
Leaf adaptation
Leaf venation
Eudicot
- Pinate (feathery)
- Palmate (palm)
- Netted
- provides more support for the leaves
Monocot
- Parallel