Skip to main content
Chapter 38
Transport of materials in plants
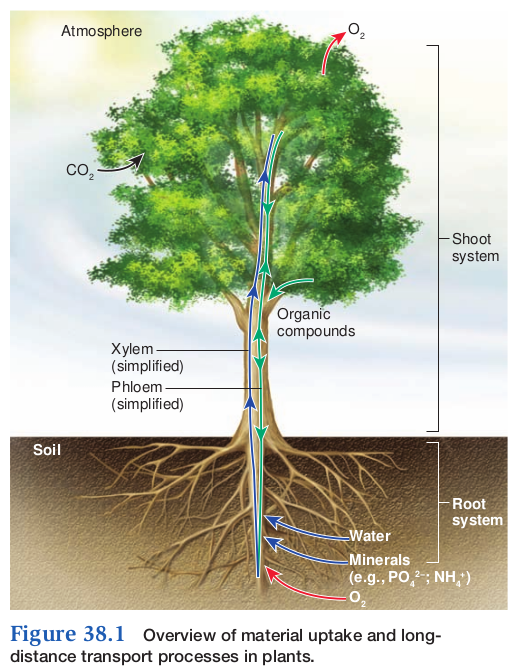
- Root system absorbs water and dissolved minerals from the soil
- Shoot system takes CO2 from the atmosphere via stomata
- Photosynthetic cells use these materials to produce organic compounds needed for growth and reproduction
- long-distance transportation occurs withing the plant body using a continuous system of conducting materials
- Xylem
- transport water and dissolved minerals
- Only goes up
- Phloem
- transports food and other solutes (hormones)
- Goes up and down
Importance of water
- Photosynthesis
- support of plant organs
- conduction
- cell elongation
- most chemical reactions
- Average plant is 90% water
- Solvent for most substances
Properties of water
- Polar molecule
- Hydrogen bonding
- Cohesiveness
- Adhesiveness
- Temperature Stabilizer
- Transport medium
- Best biological solvent
- Occurs in all 3 forms of matter within earth's temperature range
Principles of movement
- Bulk\Mass flow
- Mass movement of liquid cause by pressure and\or gravity
- Ex: leaching
- movement of ion though soil to plant roots
- Faster than diffusion
- Diffusion
- high concentration > low concentration
- Simple diffusion
- Movement of molecules through a phospholipid bilayer down a concentration gradient
- Facilitated Diffusion
- transport of molecules across a plasma membrane down a concentration gradient with the aid of membrane protiens
- Osmosis"gatekeeper"
- Diffusion across a selectively permeable membrane in response differences in solute concentration
- simple diffusion of water does not occur rapidly enough for rapid expansion of plant cells
- Aquaporins
- protein channels that allow facilitated diffusion of water
Tissue-level transport
- trans-membrane transport
- export of material via membrane proteins, followed by import of the same substance by an adjacent cell
- Ex. Auxin transport aided by carrier protiens
- Symplastic Transport
- Movement from cytosol of one cell to cytosol of another cell via plasmodesmata
- Cytosol
- Everything inside the cell wall
- Apoplastic transport
- movement along cell walls and inter-cellular spaces
- Ex: water and disolved minerals
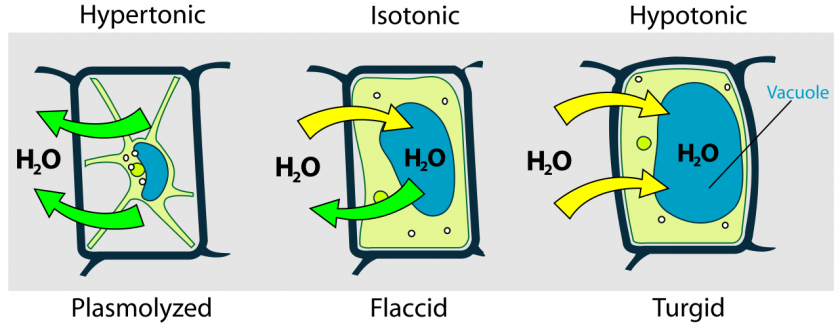
Cellular water content
- water content of plant cells depends on osmosis, which depends on:
- Solute concentration
- Turgor preassure
- hydrostatic pressure that increases as water enters plant cells
- cell walls restrict the extent to which the cells can swell
-
- Turgid plant cell has cytosol full of water and plasma membrane pushes up against the cell wall
- Plasmolyzed cell has lost so much water that turgor pressure is lost and the plasma membrane no longer presses on the cell wall
Water potential
- Potential energy of water
- Water moves from highest to lowest water potential
- affected by
- pressure
- solute concentration
- other factors (damage, temperature)
- Concept used in 2 ways
- to understand the movement of water into and out of cells (cellular water potential)
- to understand the movement of water