Chapter 40
Intro to Animal Structure(Form) & Function
Key concepts
- organization of animal bodies
- the relationship between structure and function
- homeostasis
All Animals:
- Exchange materials with their surroundings
- Obtain energy from organic molecules
- synthesize complex molecules
- reproduce themselves
- detect and respond to signals in their immediate surroundings
Levels of Animal Organization
- Cellular
- Phylum Porifera
- Tissue
- Phylum Cnidaria
- Phylum Ctehotophora
- Organ System
- All advanced animal groups
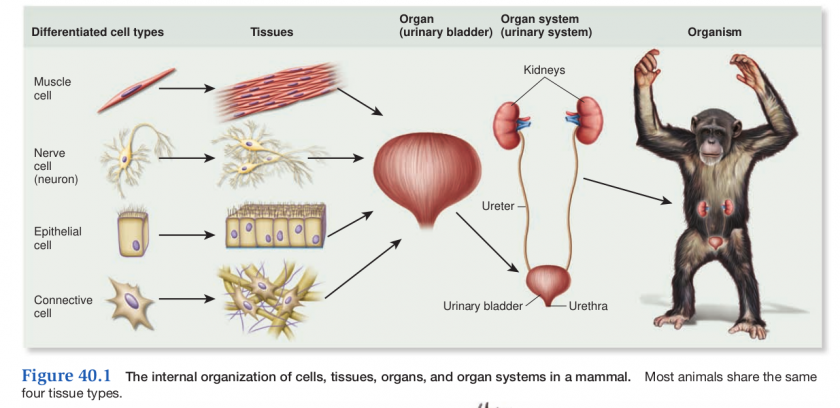
Internal Organization of Animals
- Cells with similar properties group together to form tissues
- Tissues combine together to form organs
- Organs are linked together to form organ systems
- Organ Systems form an organism
Tissues
Tissue
- An association of many cells that have a similar structure and function
Types
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Nervous tissue
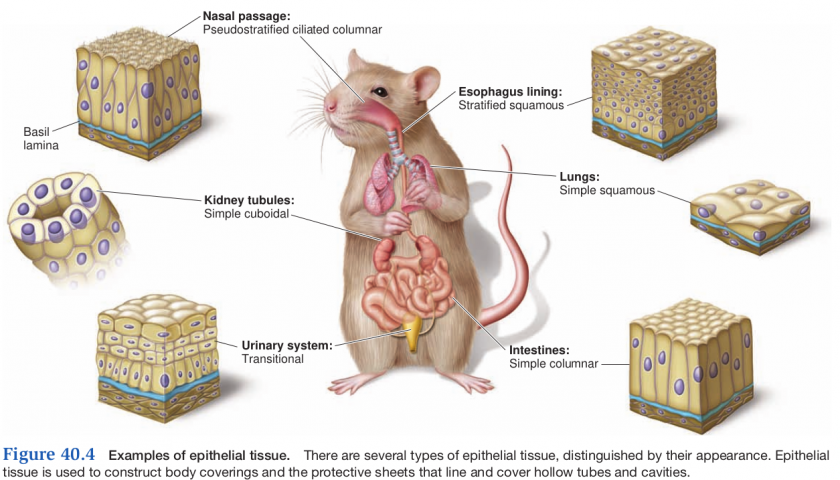
Epithelial
- Sheets of densely-packed cells that:
- cover the body or enclose organs
- line the walls of the body cavity and organs
- Specialized to protect and secrete/absorb ions and organic molecules
- cells have a variety of shapes
- cuboidal
- squamous
- columnar
- arranged to form different types of tissues
- simple
- one layer
- stratified
- multi layer
- pseudo-stratified
- one layer, but appears stratified
- simple
- All are asymmetrical or polarized
- One side rests on the basal lamina (basement membrane)
- the other faces the environment
Types of Epithelial Tissue
- Simple squamous
- one layer of flat cells
- Simple cuboidal
- one layer of square cells
- Simple columnar
- single layer of rectangular cells
- Pseudo-stratified columnar
- 1 cell thick with all at basement barrier
- Stratified squamous
- multi-layered flattened cells
- Transitional
- stretchable tissue
All may be involved with secretions/absorption/protection