Chapter 26
Overview
- Taxonomy and Systematics
- Phylogenetic Trees
- Horizontal Gene Transfer
Taxonomy
The Science of describing, naming, and classifying living an extinct organisms and viruses.
Systematics
Study of biological diversity and the evolutionary relationships among organisms, both extinct and modern.
- Taxonomic groups are based on hypothesis regarding evolutionary relationships from systematics
- Hierarchical system involving successive levels
- Each group at any level is called a taxon
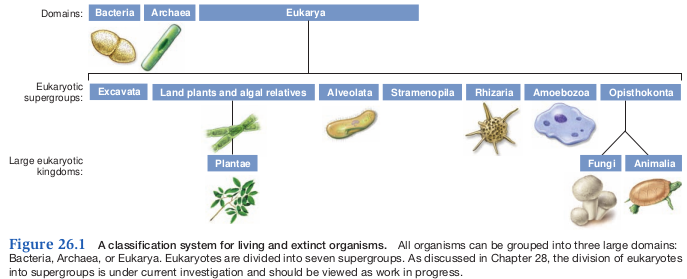
- Highest level is Domain
- All life belongs to 3 domains
- Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
- The Eukarya Domain is often divided into Kingdoms in the next level
This is typically called the 4 Kingdom concept
- The Eukarya Domain is often divided into Kingdoms in the next level
Four Kingdoms
- Domains Bacteria and Archaea
- Prokaryotic cells
- Lack nucleus
- Prokaryotic cells
- Kingdom Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animilia
- Eukaryotic cells
- True nucleus
- Eukaryotic cells
Types of cells
Prokaryotic
- Lack Nucleus
- Lacks membrane-bound organelles
- Typically singled celled
Eukaryotic
- Well defined nucleus
- Membrane-bound organelles
- internal membrane system (compartments)
Binomial Nomenclature
- Genus name + Specific epithet
- ex. Homo sapiens ('wise humans')
- Genus name is always capitalized
- Specific epithet is never capitalized
- Both names are either italicized or underlined
Phylogenetic Trees
- Phylogeny
- Evolutionary history of a species or group of species
- To propose a phylogeny, biologist must use the tools of systematics
- Trees are usually based in morphological and genetic data
- Subjective vs. Objective data
- Diagram that describes the phylogeny
- A hypothesis of evolutionary relationships among various species
- Based on available information
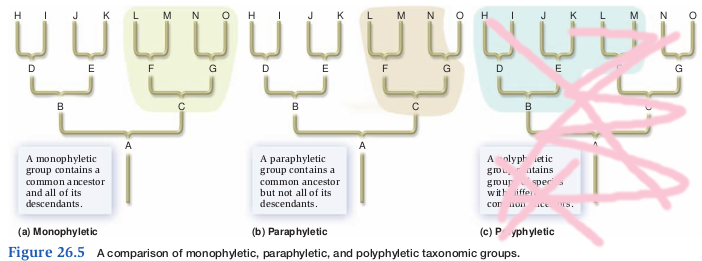
Monophyletic Group or Clade
- Group of species (taxon) consisting of the most recent ancestor and all of its descendants
- Smaller and more recent clades are nested within larger clades that have a common ancestor
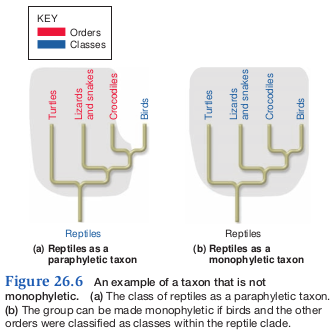
Paraphyletic group
- Contains a common ancestor and some, but not all of its descendants
- Over time, taxonomic groups will be reorganized so that only monophyletic are recognized
- Reptiles were a paraphyletic group because birds were excluded
- In the class and lab, we are going to separate birds and reptiles
Systematics
Morphological Analysis
- First systematic studies focused on morphological features of extinct and modern species
- Most of early classifications were based upon morphological features
Molecular Analysis
- Analysis of genetic data (DNA, Amino Acids, rRNA) to identify and study genetic similarities and propose phylogentic trees
- DNA and Amino Acid sequences from closely related species are more similar to each other than sequences from more distantly related species
Horizontal Gene Transfer
- any process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism (by means of asexual reproduction)
Vertical Evolution
- Changes in groups due to descent form a common ancestor (sexual reproduction)