Chapter 39
Reproduction in plants
- Most flowering plants display sexual reproduction
- Two gametes fuse to produce offspring with a unique combination of genes
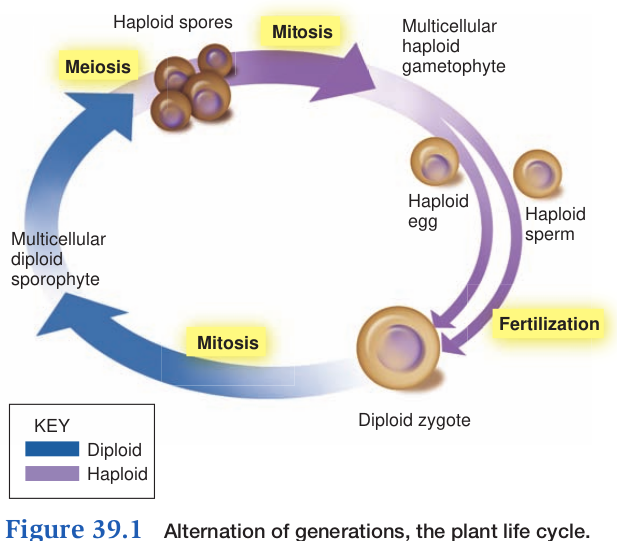
- They undergo Alternation of Generations
- Two multicellular life cycle stages
- diploid
- Spore producing sporophyte
- produces spores by meiosis
- a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores.
- produces spores by meiosis
- Spore producing sporophyte
- haploid
- Gamete producing gametophyte
- produces gametes by mitosis
- a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
- produces gametes by mitosis
- Gamete producing gametophyte
- Egg is Female
- Sperm is Male
Evolutionary Trends in the Plant Kingdom
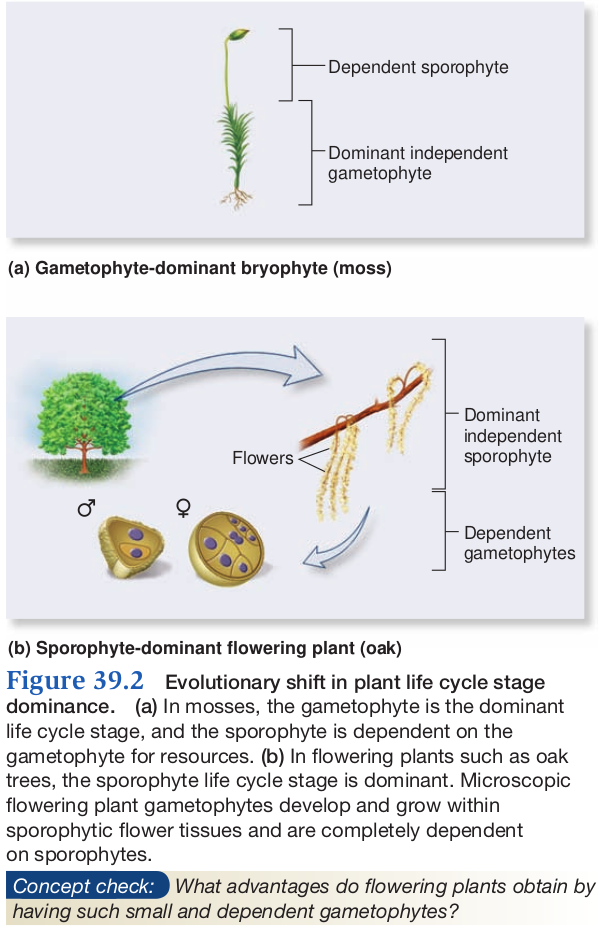
- Sporophyte has become larger, more complex
- Flowering plants
- Sporophyte independent
- Dependent gametophyte is only a few cells contained within flowers
- Flowering plants
- Gametophyte has become smaller, less complex
- Moss
- Sporophytes small and dependent on gametohyte (Dominant form)
- Moss
- Female
- 7 cells
- Male
- 2-3 cells
Flower and Sexual Cycle
- Flowers
- ONLY in angiosperms
- All sizes, shapes, colors, and aromas
- Essential process of Sexual reproduction occurs within flowers
- Meiosis/cytokenesis
- reduces chromosome number
- Syngamy (fertilization)
- restores chromosome number
- Meiosis/cytokenesis
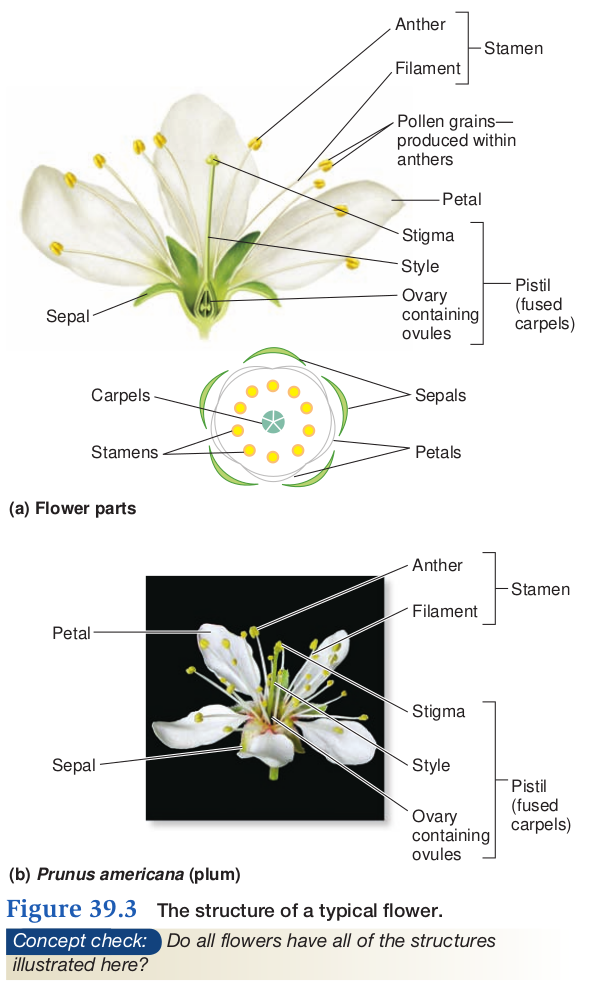
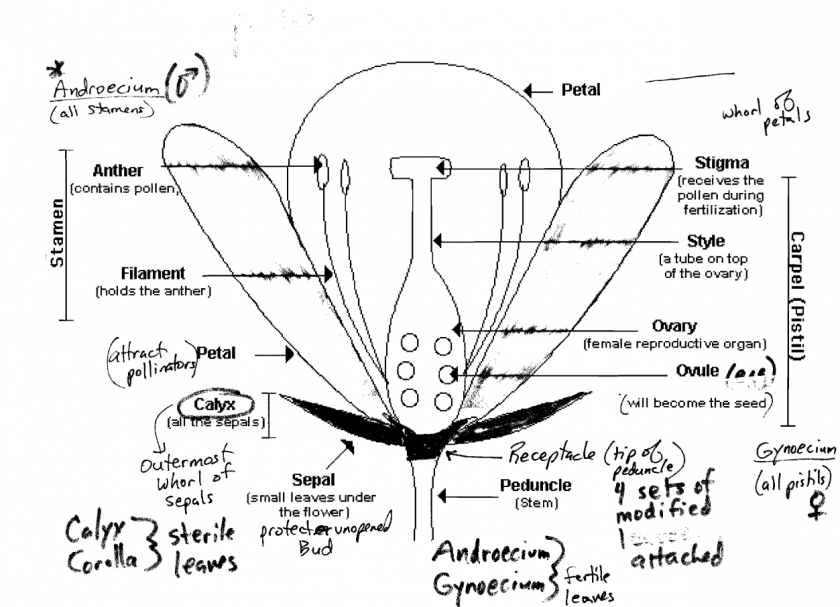
"Ideal" Flower
- Uses highly modified leaves arranged in whorls (circular) at the tip of a highly modified stem
- A flower is a highly modified determinate (short term) shoot system
- Pedical, receptical, 4 sets of highly modified leaves are all 2N and part of the sporophyte generation
- Pollen (sperm) and eggs of embryo sac are part of the 1N generation
- Pedical
- flower stalk
- Recepticle
- tip of modified stem with 4 whorls attached
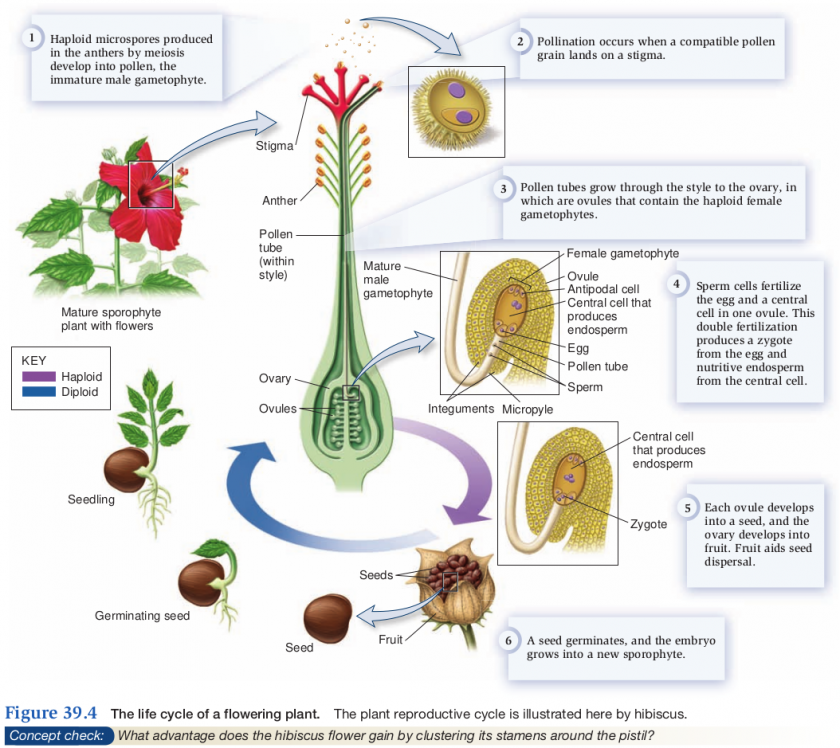
Sexual Cycle
Male
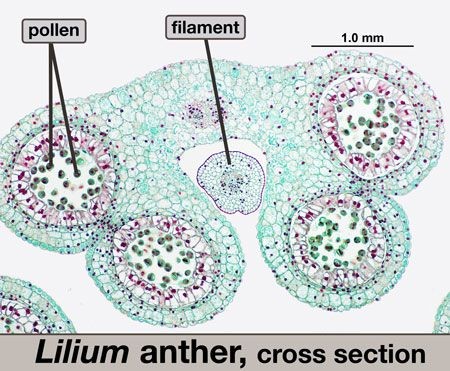
- Pollen formation
- occurs within the anther of stamen
- Anther
- Bilobed with 2 pollen chambers per lobe
- 2N microspore mother cell
- meiosis/cytokenesis
- 4 1N microspores
- Each: mitosis/cytokenesis
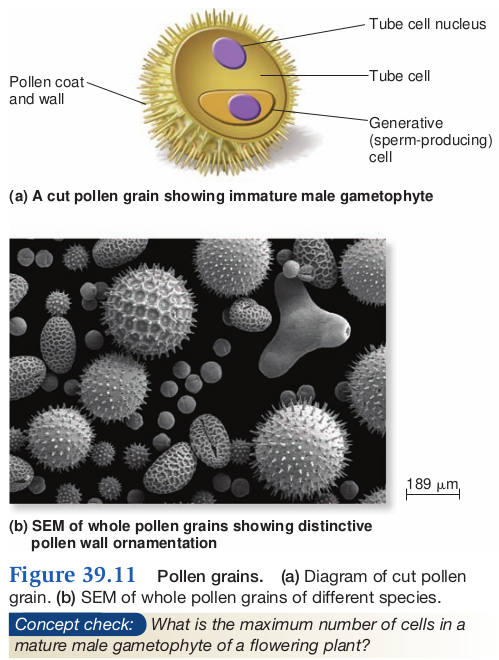
unequal and incomplete - 1N Generating cell
1N Tubecell
Male Gametophyte
Pollination
- Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma
- Self-pollination
- Transfer with the same flower or between flowers on the same plant
-
- Transfer with the same flower or between flowers on the same plant
- Cross-Pollination
- Transfer between flowers of other plants
Pollinating Agents
Mechanisms utilized for transfer of pollen
- Wind
- small/lightweight pollen
- Water
- Transfer with a few aquatic plants
- Animals
- Majority of plants
- Utilized as a "trick and reward" system
- nectar, colors, and aromas to attract animals
Female
Ovule Development
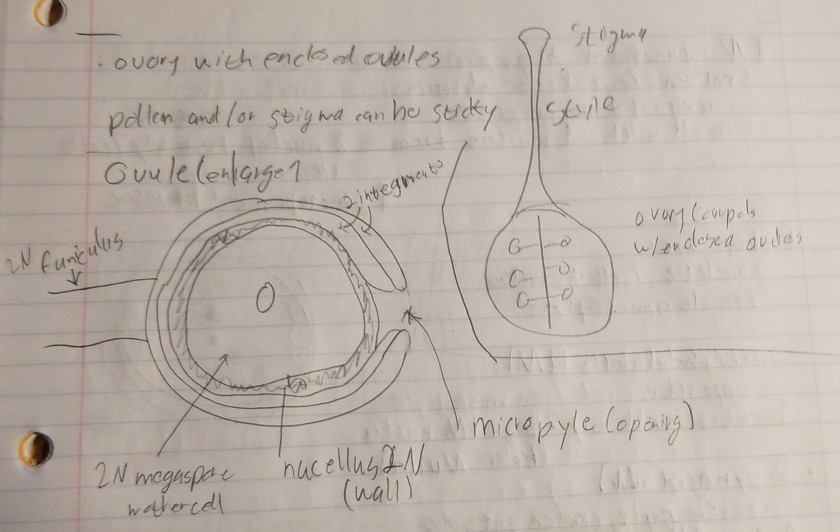
- Ovule
- future seed
- Enclosed within the ovary of pistol (carpel)
- One to many ovules per ovary
- ovary will become fruit
- Ovule attached to central axis or to wall of hollow fruit
- always enclosed
- angiosperms
- within ovule is 1 large 2N cell
- megaspore mother cell
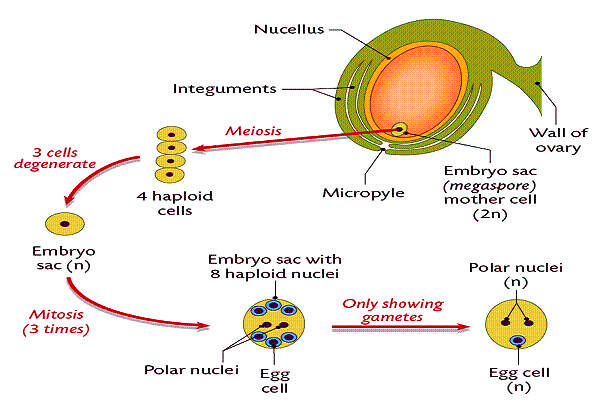
- 2N megaspore mother cell
- meisos/sytokenesis
- 4 1N Megaspores
- 3 degrade
- 2N Functional megaspore
- Series of 3 mitosis/cytokenesis cycles
Incomplete and unqueal - 7-celled embryo sac
8 nuclei
Female gametophyte
- 1N Functional megaspore
- 3 mitosis/cytokenesis divisions
- One cell with 1 nucleus becomes 8 nuclei but only 7 cells
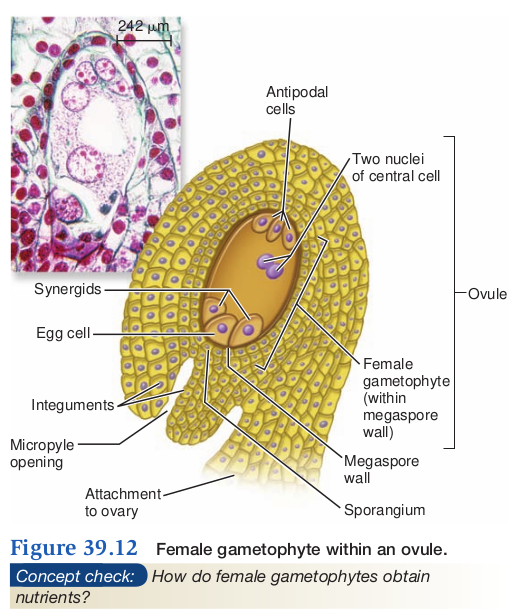
Embryo sac
- 8 nuclei, 7 cell structure
- female gametophyte
- 3 antipodal cells (1N)
- opposite end from micropyle
- 1 central cell with 2 large 1N polar nuclei
- 2 Synergids (1N)
- Micropyle end on outside
- 1 egg (1N)
- Middle at micropyle end
Syngamy (fused gametes)
- 1N egg + 1N sperm = 2N zygote (single fertilized egg)
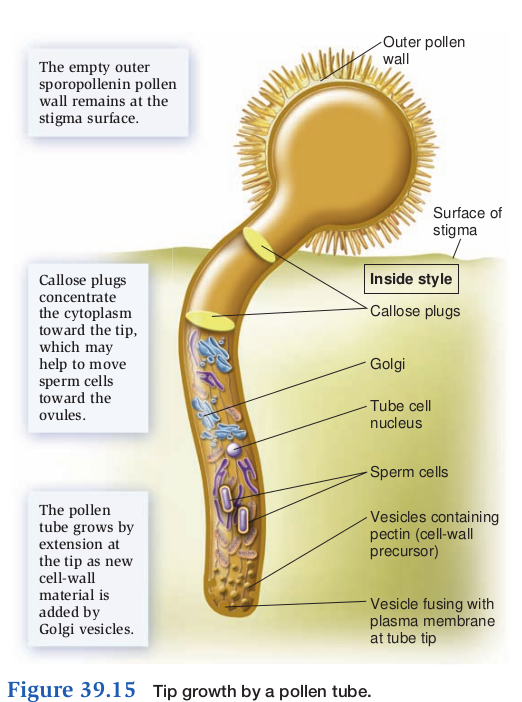
- Pollen grain germination
- tube cells form pollen tube (delivers sperm)
- generative cell divides by mitosis/cytokenesis to produce 2 sperm
- Pollen tube enters micropyle
- digests tube cell nucleus
- Pollen tube enters one synergid
- releases it's content (sperm)
- synergid ruptures
- mycropyle closes
- "Double fertilization" (double fusion)
- 1N egg +1N sperm = 2N zygote
- 1N sperm +2 1N polar nuclei = 3N primary endosperm cell
- Post fertilization with ovule
- 2N zygote grows by mitosis/cytokenesis into 2N multicellular embryo
- 3N primary endosperm cell grows by mitosis/cytokenesis into 3N multicellular endosperm
- nutrient tissue for embryo
- Ovule/ovary with 2N zygote mature/enlarges with sugars/H2O into a fruit (mature ovary) with enclosed seeds (mature ovules)
- Seed dispersal (seeds enclosed withing a fruit)
- agents
- wind
- water
- animals - majority
Seed germination
- Seed with 2N embryo enters period of dormancy
- dormancy broken by a combination of internal (hormones) and external factors (environmental)
- radical (first root) emerges and grows down
- shoot emerges and grows up