Chapter 36
Overview of plant behavioral responses
- Behavior is a response of an organism to an internal or external stimulus
- types of plant behavior
- movement
- bending,twisting, or rotating
- nutation
- rapid movement as in sensitive plants
- response to touch
- bending,twisting, or rotating
- growth
- seed germination
- seasonal production of reproductive structures
- defensive responses to attacks
- thorns, spines, chemicals
- movement
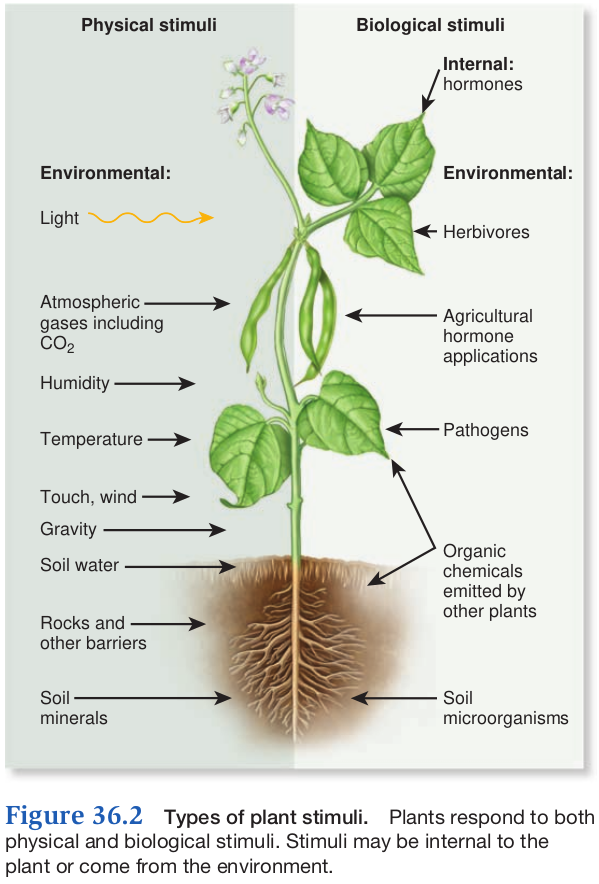
Responses to internal and external stimuli
Internal
- Internal biological clock
- circadium rhythms
- chemical signals
- transcriptions factors and other proteins or hormones
- often interact with each other and external signals
External
- light atmospheric gases (CO2 and water vapor) temperature, touch, wind, gravity, water, rocks, and soil minerals
- Herbivors, pathogens, organic chemicals from neighboring plants, and beneficial or harmful organisms
Plant Behavior
Involves internal and external stimuli
- tropism
- growth response that is dependent on a stimuli that occurs in a particular direction
- Reception molecules
- located in plant cells
- sense stimuli and cause response
Phototropism
- Growth response to light
- light causes movement of hormone auxin away from said light
- result in unequal distribution of auxin
- causing unequal cell elongation
- positive tropism
Gravitropism
- growth response to gravity
- positive tropism
- roots
- negative tropism
- shoots
- columella cells in root cap/tip region sense gravity
Thigmotropism
- Growth response to touch
- roots
- columella cells cause roots to grow around obstacles
Regulation of plant growth
Hormones
- chemical messengers that regulate plant growth
- most transported in phloem tissue
- all require an expenditure of energy on part of the plant (ATP) for transport
- interact with external environmental stimuli
Hormones control
- growth
- seed germination
- flowering
- fruiting
- shedding of leaves
- color change of leaves
Hormones of two broad categories
- growth inhibiting
- mostly fall/winter
- certain times of the year growth is not good
- growth promoting
- mostly spring/summer
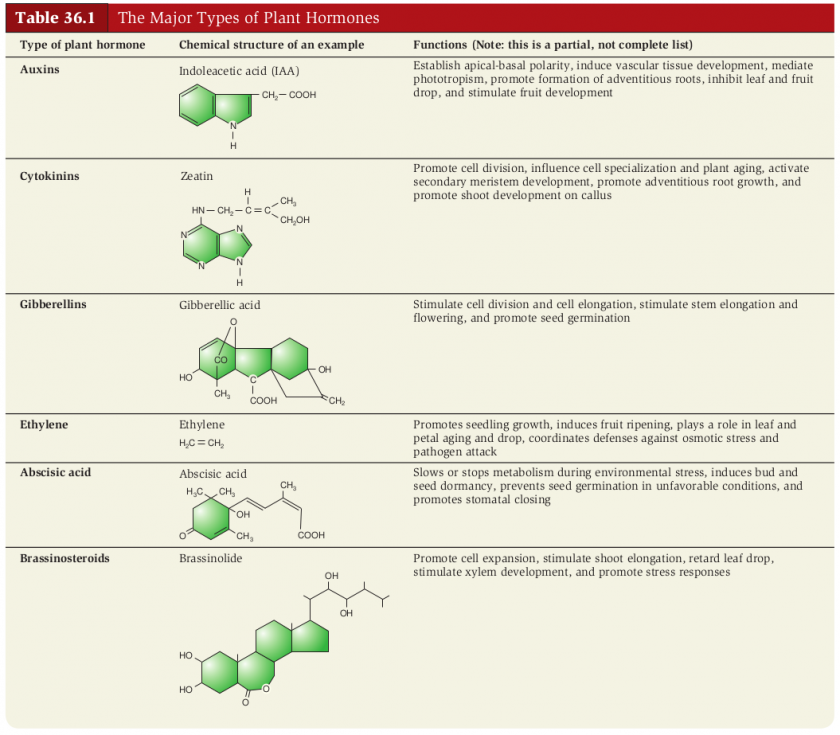
Auxins
- first group of plants hormones to be described
- growth promoting
- produced in
- shoot tips, seeds, fruits, leaves, stem
- NOT in the roots
Effects of auxin
Promotes
- cell elongation
- shoot elongation
- production of wood
- fruit development
Inhibits
- lateral bud development
- absission (falling off) of leaves, flowers, fruits
Cytokinins
- Originally detected in coconut "milk"
- growth promoting
- prodiced in
- seed, fruits, roots
Effects of Cytokinins
Promotes
- cellular division
- named derived from Cytokenesis
Inhibits
- senesence
- change of color due to breakdown of pigments
Gibberellins (giberellic acids)
- many types
- >200
- more than any other group
- growth promoting
- found throughout the plant but concentrated in seeds
Effects of Gibberellins
Promotes
- stem elongation by cell division and cell elongation
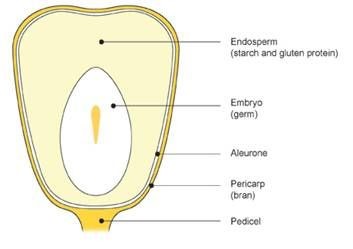
- intake of water causes swelling and embryo hydration
- embryo secretes gibberellins
- gibberellins transported to cells of aleurone layer to secrete enzyme
- (alpha-amaylase) for breakdown of endosperm (starchy stored food) to glucose
- embryo will respire glucose to produce ATP
- embryo is directing the timing of plant germination
- Advantage seed plants
Brassinosteriods
- growth promoting
Effects of Brassinosteriods
Promotes
- cell expansion
- shoot elongation
- xylem tissue development
- stress response
Inhibits
- leaf abscission
Abscisic Acids (ABA)
- Growth inhibiting
- found in large quantities in seeds. mature leaves, and dormant buds
Effects of ABA
Promotes
- senesence
- production of storage molecules in seeds
Inhibits
- cell elongation
- alpha-amaylase production
Ethylene
- growth inhibiting
- actually a gas produced by incomplete metabolism
- interacts with the 4 growth promoting hormones to determine cell size and shape
Effects of Ethylene
Promotes
- fruit ripening
- abscission of leaves, fruits, flowers
Seed germination
- requires breaking of dormancy
- combination of internal and external factors
Internal
- hormones
- stored food
- H2O absorption
- embryo swelling
External
- sunlight
- temperature
- longer day light
- soil moisture
Generalized Seed
- Seed coat(s)
- as seed coat cracks
- Radical comes out first
- then then shoot
Seedling
- result of cellular reproduction and increase size
- internal development
- cells>tissues>organs>organism